A Deep Dive into 14 Essential Electrical Components

More from the Category
Electronics and electrical engineering are the driving forces behind many technological innovations shaping our modern world. Understanding the fundamentals of these fields begins with a solid grasp of the essential electrical components and their roles in building and maintaining functional circuits. These components—from resistors and capacitors to transistors and integrated circuits—form the foundation of every electronic device we use today.
Whether you’re a beginner looking to build a strong foundation or an experienced engineer seeking to expand your knowledge, this guide offers a deep dive into 14 essential electrical components and their real-world applications.
1. Resistor
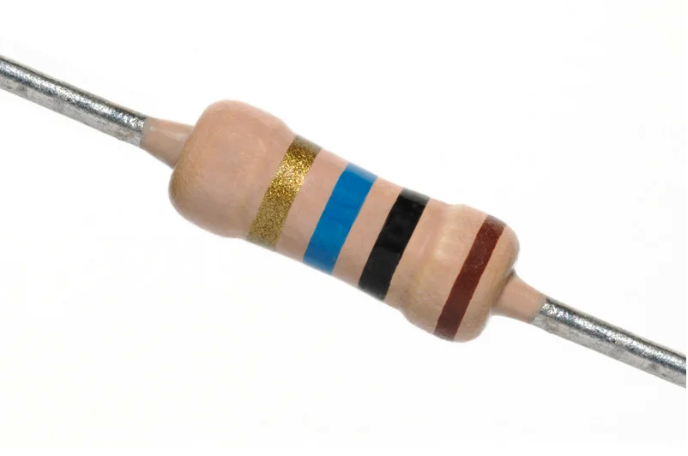

A resistor is one of the most common electrical components used in electronic circuits. It limits current flow, divides voltage, and provides load for other devices. Resistors are available in carbon film, metal film, wire-wound, and surface-mount formats, each suited to different use cases.
Series Resistance Calculation
When connected in series, resistor values are simply added:
Rt=R1+R2+R3+…+RnR_t = R_1 + R_2 + R_3 + \ldots + R_nRt =R1 +R2 +R3 +…+Rn
For example, two resistors with values 10 Ω and 15 Ω in series yield a total of 25 Ω.
Parallel Resistance Calculation
In parallel, the formula changes:
1Rt=1R1+1R2\frac{1}{R_t} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2}Rt 1 =R1 1 +R2 1
The total resistance is always less than the smallest individual resistor, which is a critical concept when designing efficient electrical components for load distribution.
Want to learn how to read resistors? Check out this article!
2. Capacitor
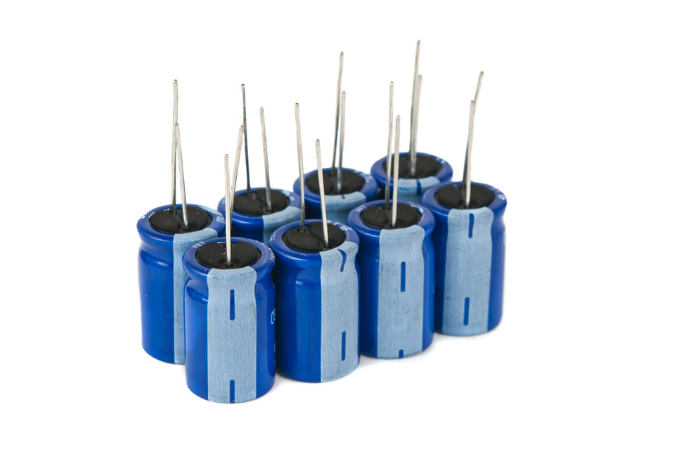

A capacitor is a fundamental electrical component that stores energy in an electric field. It consists of two plates separated by a dielectric, such as ceramic or electrolytic material. Capacitors are essential in power supply smoothing, timing circuits, and signal filtering.
Understanding Capacitance
The relationship is defined as:
C=QVC = \frac{Q}{V}C=VQ
Where CCC is capacitance, QQQ is charge, and VVV is voltage. Capacitance is influenced by plate size, distance, and dielectric properties.
Capacitors come in various types—ceramic, tantalum, electrolytic, and film—each chosen based on capacitance, voltage ratings, and environmental suitability.
3. Inductor
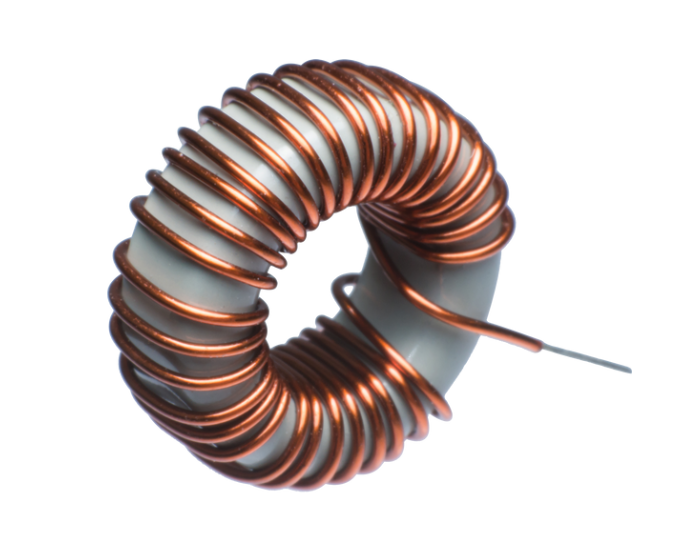

Inductors are passive electrical components that store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through a coil. They're widely used for filtering noise, energy storage in power supplies, and in motor control circuits.
Voltage and Current Relationship
The behavior of an inductor is governed by:
V=LdIdtV = L \frac{dI}{dt}V=LdtdI
This means voltage across the inductor increases with a faster rate of current change. Inductors come in air-core, iron-core, and toroidal formats, depending on the current capacity and application.
4. Diode
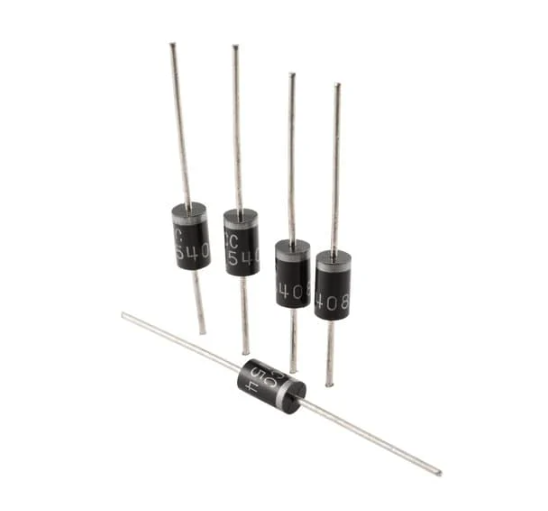

Diodes are semiconductor-based electrical components that permit current flow in only one direction. They’re essential in AC to DC conversion, voltage regulation, and circuit protection.
Forward Voltage and Breakdown Voltage
- • Vf (Forward Voltage): Minimum voltage required to conduct (e.g., 1.8 V for red LEDs).
- • Vb (Breakdown Voltage): Maximum reverse voltage before failure.
- Diodes are made from materials like silicon, germanium, or Schottky metals and are selected based on current/voltage ratings and switching behavior.
5. Transistor
Transistors are versatile electrical components used to amplify or switch electronic signals. They are made by doping semiconductor materials to form p-type and n-type junctions.
Pin Configuration
- • Collector (C): Main current input
- • Base (B): Control terminal
- • Emitter (E): Output to ground or load
- Applying a small base voltage allows current to flow between collector and emitter. Transistor types include bipolar junction (BJT), field-effect (FET), and insulated-gate bipolar (IGBT) transistors.
6. Integrated Circuit
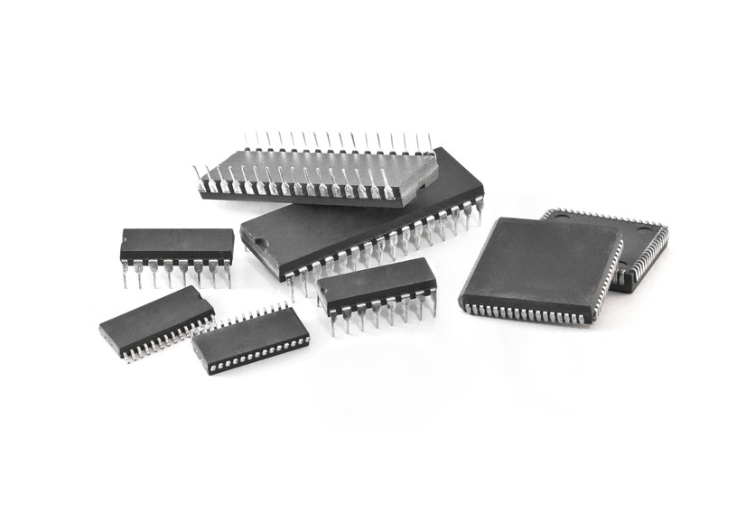

An integrated circuit combines multiple electrical components—transistors, resistors, capacitors, and diodes—on a single chip. ICs are the brains of modern electronics and power everything from microprocessors and memory to analog controllers.
IC Types
• Digital ICs: Handle binary logic and data (e.g., processors, memory).
• Analog ICs: Amplify or filter continuous signals (e.g., op-amps).
• Mixed-signal ICs: Combine analog and digital functions.
ICs are packaged in surface-mount or through-hole formats and scaled from SSI to VLSI, enabling powerful functionality in compact designs.
Looking to program integrated circuits? Check out this article!
7. Transformer
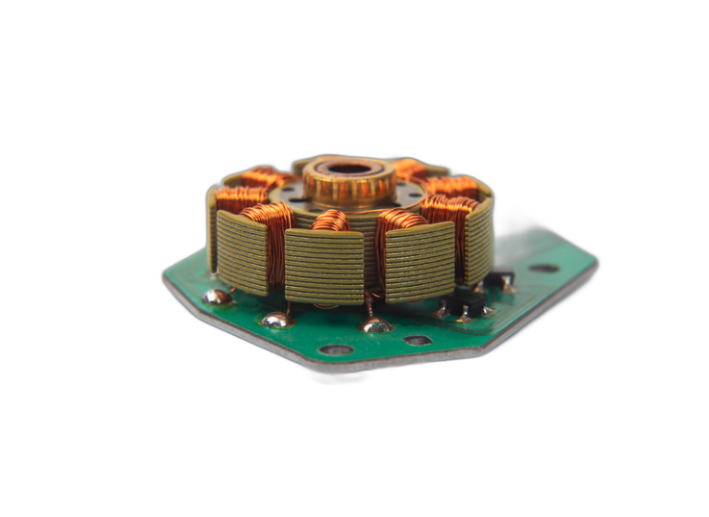

Transformers are passive electrical components that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. They're used to step up or step down AC voltages and isolate sections of a system.
Ideal vs. Real Transformers
- • Ideal: 100% energy transfer; follows:
- VsVp=NsNp\frac{V_s}{V_p} = \frac{N_s}{N_p}Vp Vs =Np Ns
- • Real: Includes losses from heat, resistance, and core hysteresis. Efficiency ranges from 95–99%.
- Transformer types include step-up, step-down, isolation, and autotransformers, each serving different voltage regulation roles.
8. Relay
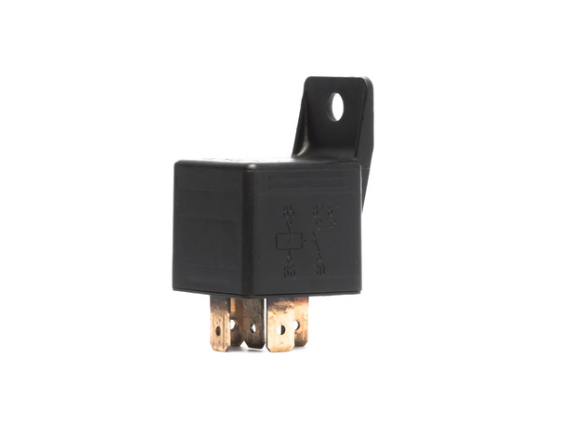

A relay is an electromechanical electrical component that switches a high-power circuit using a low-power signal. It consists of a coil that creates a magnetic field, closing or opening contacts in another part of the circuit.
Relay Variants
• Electromechanical: Traditional armature-based design
• Solid-state: Uses semiconductors for faster, contactless switching
• Reed: Fast-response, glass-encased switches ideal for low-current
Relays also come in configurations like SPST, SPDT, and DPDT, and in types like time-delay and latching.
9. Fuse
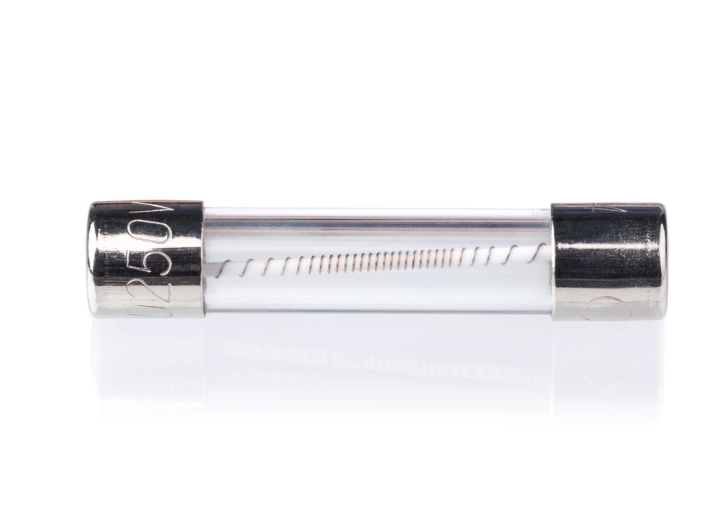

Fuses are sacrificial electrical components that break the circuit when current exceeds safe levels. Inside, a thin wire melts, interrupting power flow to prevent component damage and fire risks.
Types of Fuses
• Fast-blow: Respond instantly—ideal for sensitive electronics
• Slow-blow: Handle brief surges, used in motors and power supplies
• Resettable (PTC): Automatically reset when cooled
Choosing the right current, voltage, and breaking capacity ensures safety and reliability in diverse electrical systems.
10. Circuit Breaker
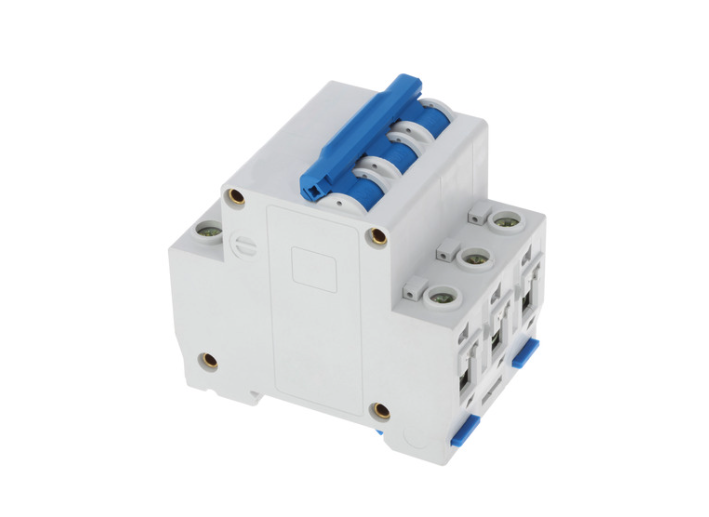

Circuit breakers are protective electrical components that trip open during overcurrent events. Unlike fuses, they are reusable and often include manual reset functions.
Types of Breakers
• Thermal-magnetic: Bimetallic and magnetic trip mechanisms
• Magnetic-only: Rapid response for short circuits
• Electronic: Offer programmable trip settings and diagnostics
Available in low-, medium-, and high-voltage forms, circuit breakers are essential for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
11. Battery
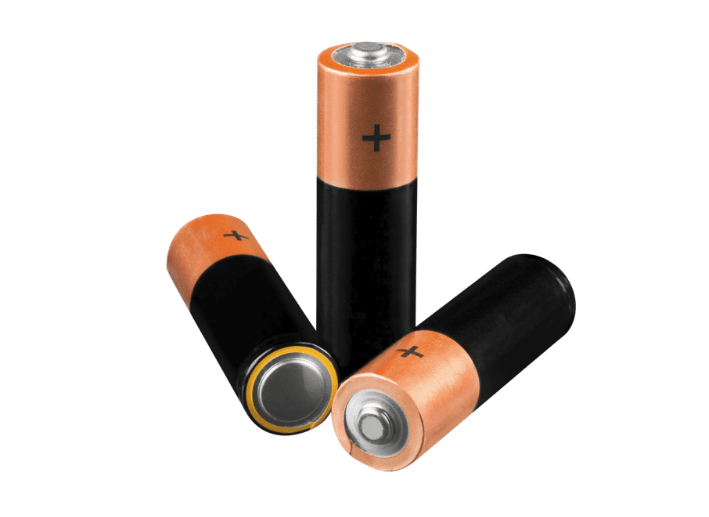

Batteries are energy-storing electrical components that convert chemical energy into electrical energy using electrochemical cells.
Common Battery Types
• Alkaline: Long-lasting, ideal for home electronics
• Lithium-ion: Rechargeable, high energy density
• Lead-acid: Used in automotive and backup systems
• Nickel-cadmium: High-discharge for tools and emergency lighting
Batteries are classified as primary (single-use) or secondary (rechargeable), chosen based on load requirements, lifespan, and environmental impact.
12. Switch
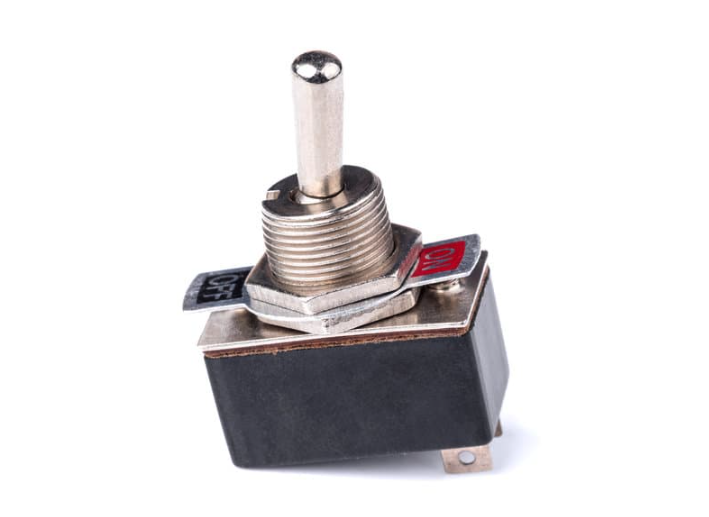

Switches are control-based electrical components used to open or close a circuit manually or electronically.
Switch Types
• Rocker: Used in power strips and appliances
• Toggle: Durable, common in vehicles and machines
• Pushbutton: Control panels and electronics
• Rotary, Slide, and Reed: Used for multi-position or magnetically actuated switching
High Voltage Considerations
Proper insulation, spacing, arc containment, thermal management, and regulatory compliance (e.g., IEC, NEMA) are critical when using switches in high-voltage systems.
Interested in high-voltage switchboards? Check out this article!
13. Oscillator
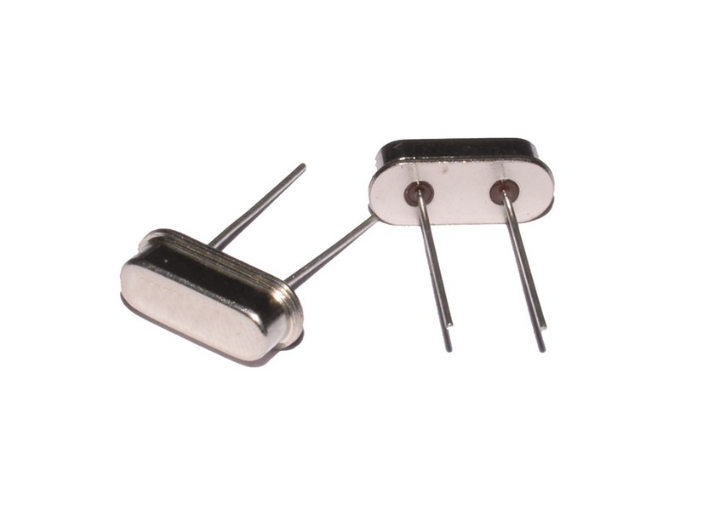

An oscillator is an active electrical component that generates continuous waveforms without external input. An oscillator converts DC power into an AC signal at a defined frequency.
Oscillator Types
• Crystal: Quartz-based for precise timing
• RC and LC: Audio and RF circuits
• Voltage-controlled: Adjustable frequency output
Output Modes
- • Single-ended: One signal and a ground—simple, but less noise-tolerant
- • Differential: Two opposing signals—superior noise immunity, ideal for communication systems
14. Transducer
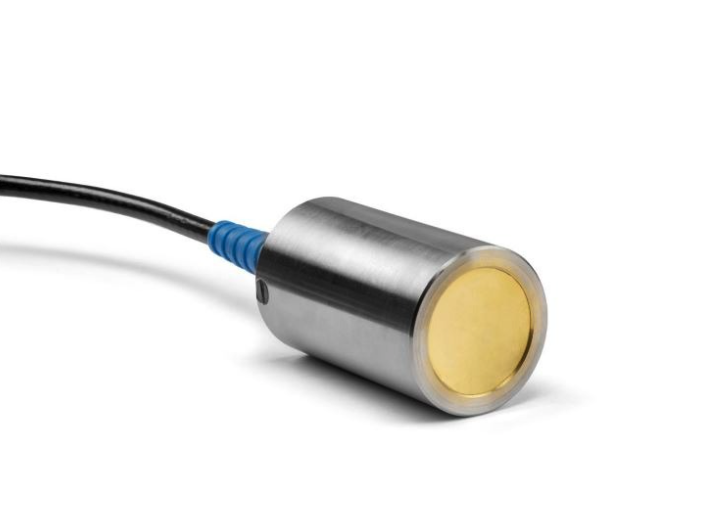

Transducers are conversion-based electrical components that change one form of energy into another. They are critical in sensing, control, and signal transmission applications.
Types of Transducers
• Piezoelectric: Converts mechanical stress into voltage
• Electromagnetic: Uses magnetic fields to generate current
• Thermoelectric: Converts temperature differences into voltage
Transducers can be active (self-generating) or passive (require external power). Proper sensitivity and frequency range selection is vital for accuracy and efficiency.
Powering Innovation Through Understanding
From tiny fuses and transistors to complex integrated circuits and transformers, each electrical component in this guide plays a vital role in powering, regulating, and protecting electronic systems. Understanding these 14 essential electrical components allows engineers and enthusiasts alike to design, troubleshoot, and innovate with confidence.
Partner with Microchip USA to Power Your Success
At Microchip USA, we understand the challenges of managing supply chains, sourcing obsolete parts, and staying ahead in an ever-evolving industry. As an experienced independent distributor of electrical components, we specialize in supplying difficult-to-find and obsolete parts.
Whether you’re working on a cutting-edge design, maintaining legacy systems, or simply trying to keep your production line moving, our expert team is here to help you succeed.
Let us support your inventory needs with proactive service that keeps your operations running smoothly. Contact us today!


